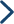
Ⅰ、 CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 → Ca2+ + 2HCO3-
Ⅱ、 Ca2+ + 2HCO3- → CaCO3↓ + H2O + CO2↑
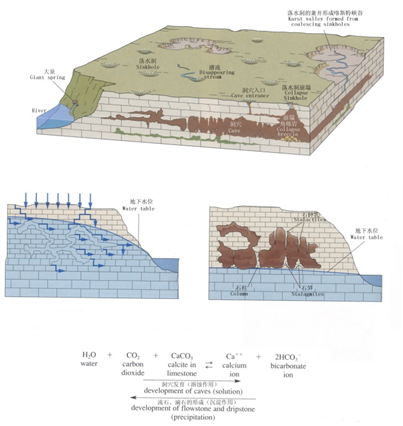
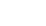
It generally refers to water and gravity’s corrosion and erosion as well as the transportation and sedimentation of soluble rock, and mainly it is represented by carbonate rocks.During this process, chemical corrosion and mechanic erosion happens simutaneously, supplementing each other. The corrosion of carbonatite is a reversible chemical reaction, referring to the process that the soluble components of carbonatite immigrate into water and are transported in form of ions and molecules under the action of natural water. The chemical reaction can be expressed as follows:
I. CaCO3+H2O+CO2 → Ca2+ + 2HCO3-
II. Ca2+ + 2HCO3- → CaCO3↓+H2O+CO2↑
When water with dissolved CaCO3 oozes from fissure of stratum, CO2 escapes due to the change of water temperature and pressure, in this way, CaCO3 in aqueous solutions will sediment to form stalactite.