Types of caves
Classification of Caves
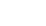
(1) According to hydrodynamic zone, it can be classified into vadose zone cave, shallow saturated zone cave, deep saturated zone cave (deep phreatic zone) and pressure bearing zone cave.
(2) According to hydrology features, it can be classified into fossil cave and underground river cave.
(3) According to geometric morphological characteristics, it can be classified into vertical cave, lateral cave and composite cave.
(4) According to the geomorphic features of cave development, it can be classified into karst peneplain cave and karst mountainy cave.
(5) According to the measured length of cave, it can be classified into small cave (<50m), middle cave (50 to500m), large cave (500 to 5000m) and super-large cave (>5000m).
2- Multilayer karst cave
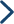
When the crust raises upwards, the underground water table decreases, the underground river will continue down-cutting to form new underground riverway, while the original underground riverway will be raised upwards into draughty cave (fossil cave); if there are several times of intermittent uplift, there will be multilayer karst cave.
3-Fossil cave
It is often called draughty cave or dry cave which means that the cave has separated itself from ground water table. The caves which had been originally developing in the underground water level belt or shallow saturated zone are raised upwards to vadose zone because of the regional uplift or the decline of underground water level, and the underground river gradually unwaters, but the karstification still works.
4-Underground river cave
It refers to the cave that is developing now and is half or completely filled with water, also including the cave system formed by linking fossil cave and underground river. Having main characteristics of river, the underground river is a karst underground passage owing turbulent features and its own water catchment area. The underground river may not have obvious entrance and exit, and it may not be a passage allowing people to come in.
The underground river cave (system) is often featured by layer. Normally on the upper layer is the fossil cave; whereas, on the lower layer is underground river cave which is still developing.