Modern research method for earth science
(1) Field work, the most basic and important link in earth science.
(2) Instrument observation, an important means to acquire qualitative and quantitative materials of study object for earth science.
(3) Geodetic survey, including geodetic leveling, geodetic triangulation, ocean sounding technology (sonar), laser ranging, GPS, etc.
图中文字:
| Comparison of world top 4 satellite navigation systems | ||||
| GPS satellite navigation system | GLOWASS navigation system | Compass (North star navigation system) | Galileo navigation system | |
| Researched & developed by such countries as… | American | Russia | China | EU |
| Historical origin | It was developed by American military and finished construction in 1994. | It was developed from the early 1980s, and was put into operation in 1995, similar to the principle and function of GPS system. | It began from the middle of 1980s, and finished construction of the first generation in 2003; the second generation is under construction. | It was put forward in the 1990s and approved in 2002, and its construction began in 2008. |
| Cover area | Global and all-weather conditions | Global | The first generation only covers China and the surrounding countries; While the second generation will cover the whole world. | Global |
| Satellite quantity | 24 satellites in operation and 4 satellites for standby | 24 satellites (satellites quantity in operation can’t reach the designed number for lacking of funds, there are only 6 ones in operation, currently, there are 17 ones in operation) | There are only 3 satellites for the first generation (two of them are in operation, and the other is for standby); there are 5 geostationary satellites and 30 non-geostationary satellites after finishing the construction of the second generation. | 27 satellites in operation and 3 satellites in preparation (still under construction) |
| Location accuracy | 10m | 16m for point positioning accuracy horizontally and 25m vertically. | The 3D positioning accuracy of the first generation is within decades of meters, while that of the second generation is 10m. | The positioning error is no more than 1m. |
| User capacity | GPS is a unidirectional ranging system, and the user’s equipment can perform range-based localization as soon as receiving the navigation message from navigation satellites, therefore, it can fit infinite users. | Infinite | The first generation Compass is an inquiry-responding system with active bidirectional ranging; its users are limited to less than 1 million. | Infinite |
| Scope of users | For both military and civil use, mainly for military use | For both military and civil use, mainly for military use | For both military and civil use, mainly for civil use | For both military and civil use, mainly for civil use |
| System progress | The arrangement of GPS satellite navigation system has been finished in 1994. For the moment, the second generation is just under research. | So far, there are 17 satellites in-orbit operation, which would be in place in 2008 as planned. | Until now, 5 Compass satellites have been launched, the users’ need in China and surrounding districts has been met in 2008, and it will cover the whole world in 2020. | In 1999, EU declared the Galileo plan, by now, the Galileo system is under construction. |
| Advantages | Mature | High anti-jamming capability | Interactivity and openness | Accuracy |
| Business development situation | Pretty early, fully developed | Scarcely developed, almost none in China | Starting phase | Start building, and it will have a promising future with so many cooperators. |
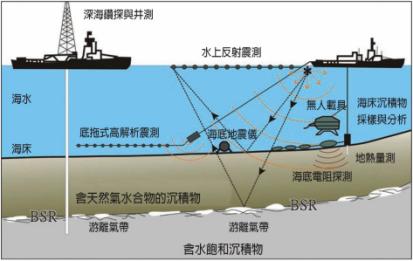
Deep-water drilling and well measurement
Water reflection-seismic exploration
Seawater
Seabed
Bottom-pull high-resolution reflection seismic
Ocean bottom seismograph
Unmanned carrier
Sampling and analysis of seabed sediments
LC measurement
Seabed resistance detection
Sediments with natural oxygen hydrate
Free gas zone
Free gas zone
Water saturation sediments
(4) Aeronautic and astronautical technologies and remote sensing technology, greatly promoting the development of earth science.
(5) Lab analysis, tests and scientific experiments, the commonly used research method adopted by all disciplines of earth science.
(6) Misering
(7) Computer technology, an indispensable research means and method.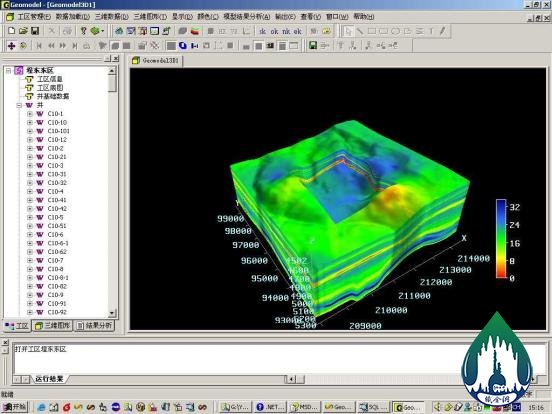
(8) Historical comparison, comprehensive analysis, method of inversion (inverted sequence), creative thinking, four-dimensional science (real world and the already disappeared world).