Geology
A science that studies earth. It studies the constituent material composition, internal structures and surface features of earth (currently mainly studying the crust of earth), all kinds of geological processes during the development history of earth as well as forms of life once living on the earth and their evolution.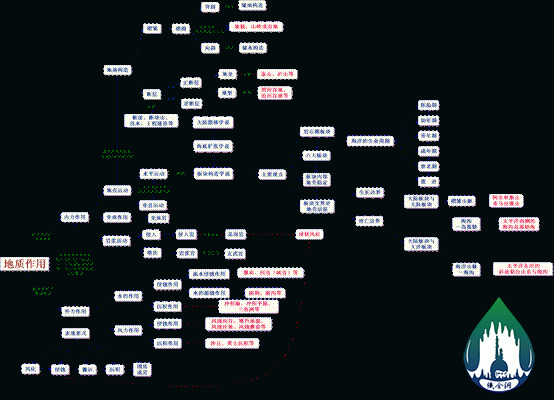
Action of water
Action of wind
Fold
Fold
Anticline
Application
Oil-bearing structure
Old and new relationship of totally different stratum
Syncline
Application
Water-bearing structure
Landform: mountain ridge or valley
Fault
Classification
Normal fault
Reverse fault
Horst
Graben
Examples
Mount Taishan, Mount Lushan, etc.
Weihe River valley, Fenhe River valley
Application
Bluff, block mountain, water exploration, engineering construction, etc.
Horizontal movement
Vertical movement
Horizontal movement rules while vertical movement is derived.
Explanation
Continental drift theory
Sea-floor spreading theory
Plate tectonics
Main opinions
Lithospheric plate
Six plates
Crust is active where the plates connect
Growing boundary
Perishing boundary
Life cycle of ocean
Embryonic period
Infancy
Adolescence
Adult
Old period
Heritage
Continental plate and continental plate
Continental plate and oceanic plate
Fold mountains
Alps and the Himalayas
Oceanic trench-island arc chain
Oceanic trench-island arc chain sea in the west of the Pacific ocean
Coast ranges-oceanic trench
The Cordillera series and oceanic trench in the east of the Pacific ocean
Invade
Intrusive rock
Representative rock
Granite
Spheroidal weathering
Eruption
Magmatic rock
Representative rock
Basalt
Erosion effect
Runoff erosion effect
Waterfall, river valley (gorge), etc.
Dissolution effect of water
Karst cave and lapie
Sedimentation
Alluvial fan, alluvial plain, delta, etc.
Erosion effect
Aeolian erosion gully, Yardang landform, aeolian erosion depression, and aeolian erosion mushroom, etc.
Sedimentation
Sand dune, loess sedimentation